Which X Ray Would Be Used to Visualize the Gallbladder
A computer displays images of where the tracer is found in the organs. An x-ray uses electromagnetic radiation to create black-and-white images of the inside of your body.

Anatomy Human Abdomen Mri Abdomen Coronal Anatomy Free Cross Sectional Anatomy Radiology Imaging Mri Diagnostic Imaging
What type of X-ray would be used to visualize the gallbladder.
. Stanford Cancer Center Palo Alto. Frequently performed to diagnose heart valve problems and is termed echocardiography to identify the. If the provider cannot see the gallbladder after certain amount of time you may be given a small.
An abdominal X-ray can spot gas and some types of gallstones containing calcium. Patient instructed to have fat-free meal evening before procedure and NPO after midnight. In some cases you may need to swallow a substance called.
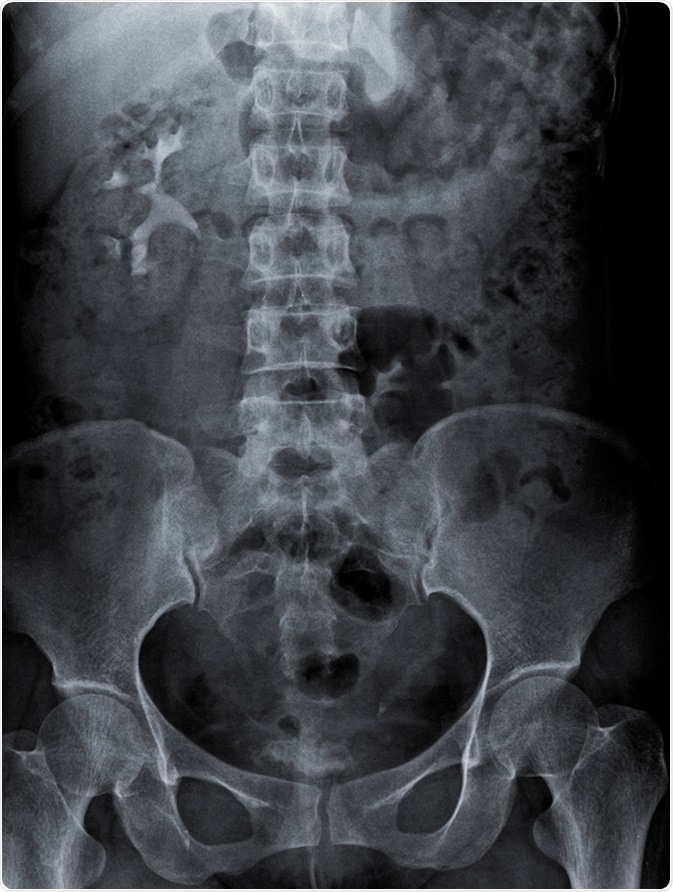
Since only 10 of gallstones are radiopaque the remaining 90 will appear as translucent on an opaque background in an abdominal X-ray. The x-ray technologist should be informed since the gallbladder might not be well visualized. How the test is performed.
X-rays are used for a multitude of reasons. Oral cholecystogram is an X-ray imaging procedure used to examine the gallbladder a sac-like organ in the right upper abdomen that stores bile before it is released through the bile ducts into the small intestines to help digest fat. This condition is somewhat uncommon and results from calcification of the gallbladder wall.
Images are taken every 5 to 15 minutes. The following day at the hospital the radiologist examines the gallbladder with a fluoroscope a special x ray that projects the image onto a video monitor. If needed intravenous cholecystography and cholangiography may be done.
A simple abdominal x-ray can be used to identify calcified gallstones. X-ray of the gallbladder made visible through the use of a radiopaque contrast medium Echography Process of using ultrasound as a diagnostic tool by making a record of the echo produced when sound waves are reflected back through tissues of different density. An X-ray of the gallbladder can be viewed through an abdominal X-ray which sometimes requires the patient to swallow a dye or have it injected into the body in order to create a clearer image of the gallbladder.
Cancer Center in South Bay. Other related procedures that may be used to diagnose problems of the gallbladder include abdominal X-rays computed tomography CT scan of the liver and biliary tract abdominal ultrasound cholecystography or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography ERCP. When the gallbladder is visualized on OCG it can also be used to number and size gallstones accurately.
The primary purpose of the OCG is to establish that the cystic duct is patent. The test was once the standard for diagnosing diseases of the GB such as gallstones but is used less frequently now. Because only 10 of all gallstones are calcified this imaging study has limited usefulness.
Radiologic examination of gallbladder using contrast medium usually iodine. Porcelain gallbladders can also be seen in plain x-rays. The study involves taking tablets containing dye contrast which outline any abnormalities when x rays are taken the following day.
Most of the time the test takes about 1 hour. It should empty freely with no obstruction after the PFM post-fatty meal. Angiography X-ray visualization of internal anatomy of blood vessels after radiopaque material injected into blood vessels Myocardial infarction MI or heart attack.
Overview A cholecystogram is an x-ray procedure used to help evaluate the gallbladder. Gastrointestinal GI Cancer Program. The oral cholecystogram study is used to diagnose problems related to your gallbladder such as gallbladder cancer or decreased or blocked bile flow in the biliary duct system of your liver.
A gallbladder ultrasound is a noninvasive and typically painless examination used to diagnose conditions related to the gallbladder. Results A normal OCG will show a normal gallbladder. Some X-ray types require that a patient swallow a dye or have dye injected into the body so the X-ray can capture a.
MRI scan is used to scan gallbladder. The procedure for getting an x-ray can vary. Your health provider may order an x-ray if they suspect gas buildup calcified gallstones or porcelain gallbladder concerns.
Sometimes patients are then asked to drink a highfat formula that will cause the gallbladder to contract and release bile. The gallbladder should visualize and be free of any solid structures such as stones polyps or tumors. At times it can take up to 4 hours.
This is an x-ray exam of the gallbladder GB a sac-like organ that stores bile that is located under the liver. The test is used to help in diagnosing disorders of the liver and gallbladder including gallstones and tumors. A physician may order an X-ray to check for certain cancers in different parts of the body by.
Clinics for Chest X-ray. Current medical practice prefers ultrasound and CT over oral cholecystography. For the procedure a special diet is consumed prior to the test and contrast tablets are also swallowed to help visualize the gallbladder on x-ray.
Currently most protocols evaluating the efficacy of gallstone lithotripsy require a visualized gallbladder on oral cholecystography OCG. You could need other tests along with an x-ray. Reasons for a Gallbladder X-Ray.
The scanner detects the rays coming from the tracer.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12296/chest_PA.jpg)
Radiological Anatomy X Ray Ct Mri Kenhub
Abdominal Radiography Radiology Key

Chest X Ray Showing Multiple Bilateral Ground Glass Opacities Download Scientific Diagram

Abdominal X Ray Showing Two Plastic Stents Double Pigtail In The Gall Download Scientific Diagram

Ribs Ap Oblique View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Contrast Medium Medicine Britannica
Gallstones Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Learn How To Read A Cat X Ray Long Beach Animal Hospital

Kidney Ureter And Bladder X Ray Johns Hopkins Medicine

X Rays Concise Medical Knowledge

Approach To The Abdominal X Ray Axr Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals
Abdominal Radiography Radiology Key
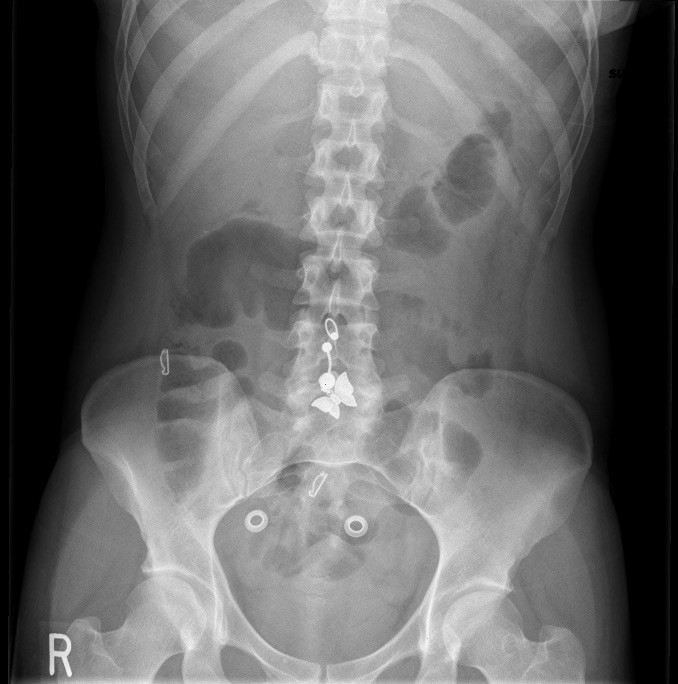
Approach To The Abdominal X Ray Axr Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals
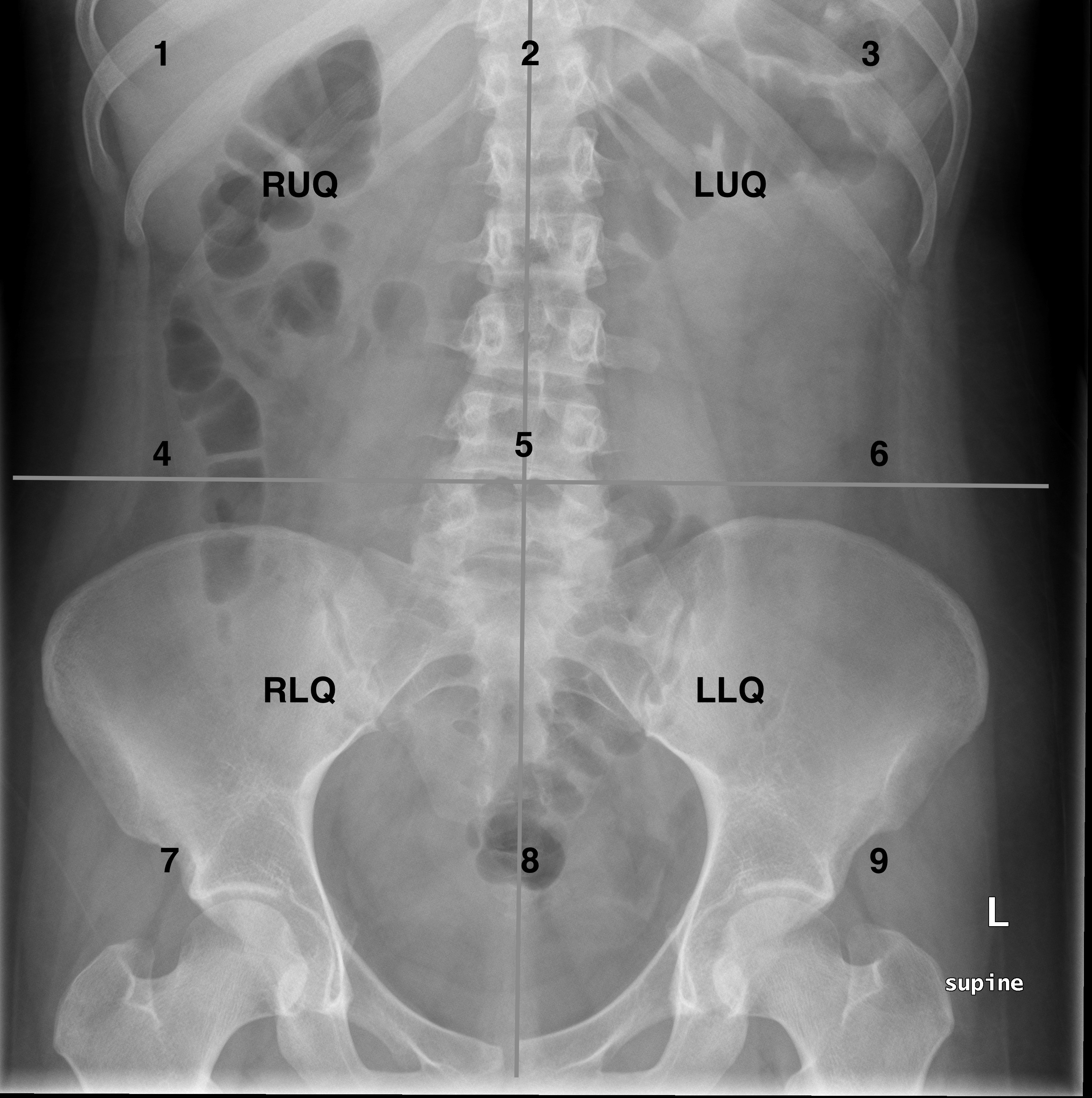
Approach To The Abdominal X Ray Axr Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals

Plain Abdominal Radiograph Demonstrating Rigler S Triad Pneumobilia Download Scientific Diagram

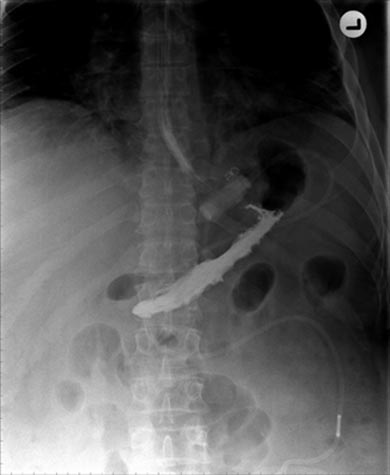
Comments
Post a Comment